In this sub module we will discuss about the importance of authentication and methods to achieve highest level of network security with ease of use. There are various techniques and protocols which aid in achieving desired security in wireless networks.
What is Authentication?
User authentication is simply proving who you are. There are many methods that can be used for authentication and it is not just for confidentiality; authentication can also be used for non-repudiation purposes. Repudiation is when there is an issue and someone tries to say they did not cause it so authentication holds people accountable. Factors of authentication include –
- Something you have
- Something you know
- Something you are
There is also multifactor/two factor authentication –
- Badge and Personal Identification Number (PIN)
- Fingerprint and password
Single Sign On
Single sign on is the ability to pass on authentication to multiple servers without having the re-enter information multiple times. However, many applications which utilize single sign on require re-entering credentials when accessing sensitive information, such as the part of the application where you can change your password. While single sign-on allows for great ease of use, it is still important to be careful how credentials are stored.
Algorithms of Encryption
Encryption is the process of taking data that is in clear text and changing it to and changing it into cypher text. Cypher text is the goal, what we want to send over the network and where we want to store sensitive data. Encryption and decryption is accomplished via mathematical algorithms, many of which are based randomly generated prime numbers. Typically, the algorithm stays the same; it’s the key that changes. Some of the encryption algorithms are –
- Triple DES – This is the replacement of original ‘Data Encryption Standard’. This is a cipher that uses three individual keys with 56 bits each. The total key length adds up to 168 bits.
- RSA – RSA is a public-key encryption algorithm. It uses a pair of keys and is considered as an asymmetric algorithm. A public key is used to encrypt message, and a private key to decrypt it.
- AES – This is the Advanced Encryption Standard approved by NIST. It is efficient in 128-bit form. It also uses keys of 192 and 256 bits for heavy duty encryption purposes.
- SHA-1 -SHA-1 is a hashing algorithm similar in structure to MD5. It produces a digest of 160 bits (20 bytes).
- HMAC – HMAC is a hashing method that uses a key in conjunction with an algorithm such as MD5 or SHA-1. Thus one can refer to HMAC-MD5 and HMAC-SHA1.
- Blowfish – This symmetric cipher breaks messages into blocks of 64 bits and encrypts them individually.
Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption
There are two main encryption types: symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption is when the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt. When using symmetric encryption, you must be able to trust the other party and find a way to get them the pre-shared key. Symmetric encryption is also good for non-repudiation.
Asymmetric encryption differs from symmetric encryption in that it has a public key and a private key. The public key is the one which is widely distributed and given out to whoever needs it and is used to publicly encrypt data. However, the private key is secret and yours alone and is used to decrypt data.
Data Hashing
Data hashing Data hashing is a one-way mathematical algorithm which allows us to obtain a string of numbers like a fingerprint that cannot be reversed. Data hashing allows for file verification and helps with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public key infrastructure is what makes use of asymmetric encryption to encrypt transmissions. In addition to assisting with encryption, public key infrastructure allows us to sign electronic documents and verify and individual is who they say they are. Public Key Infrastructure is not only a very strong tool for user authentication and encryption but is also a very good tool for non-repudiation.
Kerberos
Kerberos is considered as the ‘three-headed guard’ of a network. The three heads of Kerberos include –
- The key distribution centre
- Authentication service
- Ticket granting service
Kerberos is found in a Windows domain and relies on a trusted third party who hands out tickets which are used to authenticate.
Authentication, Authorization and Accounting
These are known as Triple A servers –
- Authentication –It is proving who you are.
- Authorization – It tells what you are allowed to access.
- Accounting – It is tracking account use and actions.
The triple A server provides a central repository for user accounts, passwords and permissions to be checked against another protocol.
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial in User Service (RADIUS) is the standard seen in most domain environments. It is what it used in order to dial in and authenticate users over VPN as well as Wi-Fi connections. RADIUS authenticates via a UDP connection and the password is only encrypted in the authentication packet and provides more accounting, so account use and actions can be tracked.
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACAS)
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACAS Plus) is a CISCO proprietary system utilizing transmission control protocol (TCP). In TACAS, the entire authentication packet is fully encrypted and allows us to set up our own CISCO independent servers and databases.
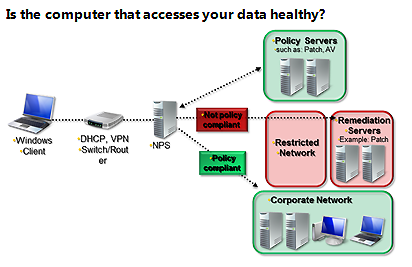
Network Access Control
Network access control is what allows or denies access to a network and comes in two forms –
- Posture Assessment – It checks client machine against set of requirements, such as making sure all machines on a network have the latest antivirus protection and/or security updates.
- 1x – IEEE protocol which requires devices to authenticate before network access.
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
These are different methods of remote authentication. Methods of remote authentication include –
- Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) – Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) is a one-way authentication for remote access connection. CHAP does not send credentials in clear text, nor does it verify the end point.
- Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) – There is also a Microsoft enhanced version of CHAP called MSCHAP that utilizes two-way authentication. Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a framework for authentication and is a standardized authentication method which allows us to configure devices to authenticate according to a network’s authentication method. EAP runs over the data-link layer and does not need an IP address.