
Proxies
Theft of information is a serious crime that can cause the loss of data and personal information. In order to prevent losses, we have proxy tools that protect our information. The web servers can at times be protected using these proxies.
The systems on the network can not get to the internet on their own and they need to have the proxy addresses for it. For example, let us assume there are many computers A,B,C,D and so on out of which one system B tries to find out any information through Google. The Proxy server will receive the information and identify its source of origin. After which it will apply the filtering guidelines to the request received. The Proxy server will then remove the flag or the IP address of ‘B’ and assign a new public address requesting Google to furnish the information.
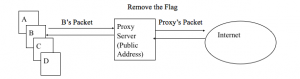
Hence, multiple computers with their private address share one public address to find out the information. If more than one computer looks for the same piece of information, each time the proxy will not go to the internet. Rather, it maintains its own temporary memory from where it will supply the required information and this is called as Caching.
The Proxy server can also be called as the Third Party Server. There are several different types of proxies that serves their own specific purpose. To name them, we have Caching Proxy Server, Web Proxy, Anonymizing Proxy Server, and Hostile Proxy.
Reverse Proxy Server
A Reverse Proxy Server is a type of proxy server that recovers the resources on client’s behalf from one or more servers. They protect the server and allows to go through the request only if it comes from a legitimate server.
The reverse proxy server can block the information if it comes from the malicious sources. In this manner, it helps to reduce the load on the original servers by caching static as well as dynamic content.
