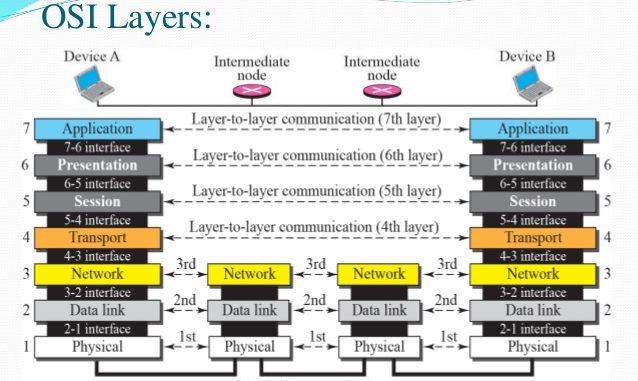
In this sub module we are going to discuss that how different protocols and devices relate to the OSI Model. There are different protocols at each layer of OSI model which aid that layer in performing the task assigned to it in a proficient manner.
OSI Network Protocol
The open systems interconnection (OSI) model was developed by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) as a model for a computer communications architecture and as a framework for developing protocol standards. The intent of the OSI model is that protocols be developed to perform the functions of each layer. Although many useful protocols have been developed in the context of OSI, the overall seven-layer model has not flourished. Instead, it is the TCP/IP architecture that has come to dominate.
Here is the OSI model protocols used at each of the seven layers –
- Layer 1, the Physical Layer: This layer is concerned with the transmission of unstructured bit stream over physical medium; deals with the mechanical, electrical, functional, and procedural characteristics to access the physical medium. The major protocols used by this layer include Bluetooth, PON, DSL, OTN, IEEE.802.11, IEEE.802.3, L431 and TIA 449.
- Layer 2, the Data Link Layer: This layer provides for the reliable transfer of information across the physical link. The protocols used by the Data Link Layer include: CSLIP, ARP, HDLC, IEEE.802.3, X-25, PPP, SLIP, ATM, SDLS and PLIP.
- Layer 3, the Network Layer: This layer provides upper layers with independence from the data transmission and switching technologies used to connect systems; responsible for establishing, maintaining and terminating connections. The network layer assists the following protocols: AppleTalk, IPX, ICMP, Internet Protocol (IPv4), Internet Protocol (IPv6), IPSec and IGMP.
- Layer 4, the Transport Layer: The transport layer provides reliable, transparent transfer of data between end points; provides end-to-end error recovery and flow control. It uses the protocols including: UDP, SPX, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), DCCP and SCTP.
- Layer 5, the Session Layer: The session layer provides the control structure for communication between applications, establishes, manages and terminates connections (sessions) between corresponding applications. The protocols used are: SAP, PPTP, L2TP and NetBIOS.
- Layer 6, the Presentation Layer: It provides independence to the application processes from differences in data representation (syntax). The following are the presentation layer protocols: XDR, SSL, TLS and MIME.
- Layer 7, the Application Layer: This layer provides access to the OSI environment for users and also provides distributed information. This layer uses following protocols: HTTP, SMTP, FTP, Telnet, DHCP, SNMP and SMPP.