What are Web Server Vulnerabilities?
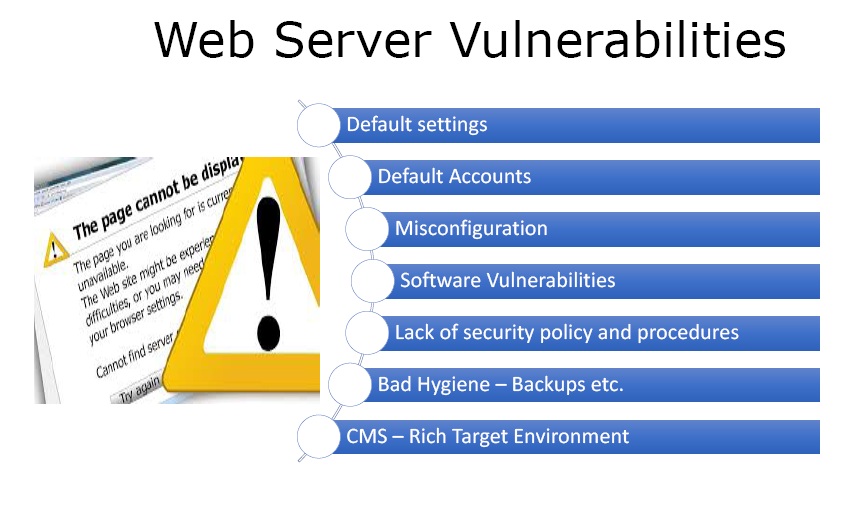
Figure 1. Web Server Vulnerability
- Default settings – A lot of hacking of web servers happen as a result of system administrator leaving settings as default user names, default passwords as well as default file allocations, file settings, file execution types, etc.
- Default Accounts – Default accounts, user names and passwords for various internet facing devices must be changed as this is a very easy way to hack the target.
- Misconfiguration – This vulnerability occurs when the system admin has not configured the server or the application on the server. This will give easy access to the server and the application.
- Software Vulnerabilities – The admin should patch the software often and reboot and maintain their service because with new software vulnerabilities it is easier for tools like ‘metasploit’ to actually crack the software vulnerabilities.
- Lack of security policy and procedures – If the company follow robust security policy and procedure it is less prone to hijacking.
- Bad Hygiene – Backups etc. – The backups and other system information not kept safely leave the system vulnerable to the hackers.
- CMS – Rich Target Environment – If one is using CMS to manage the website, one must follow strict security procedure to safeguard itself from hijackers.
What are Types of Web Servers?
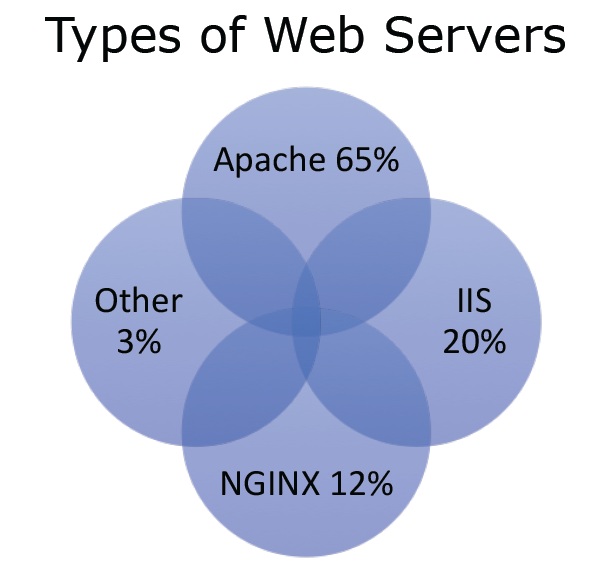 Figure2. Types of Web Servers
Figure2. Types of Web Servers
- Apache 65% – It is free and open source and thus is in reach to many. Many websites are hosted on apache because of its ease of use.
- IIS 20% – It is owned by Microsoft and its use is increasing substantially.
- NGINX 12% – For large websites like Facebook, Twitter, NGINX is used as it has good multithreading capabilities.
- Other 3%
What are Web Server Attacks Techniques?
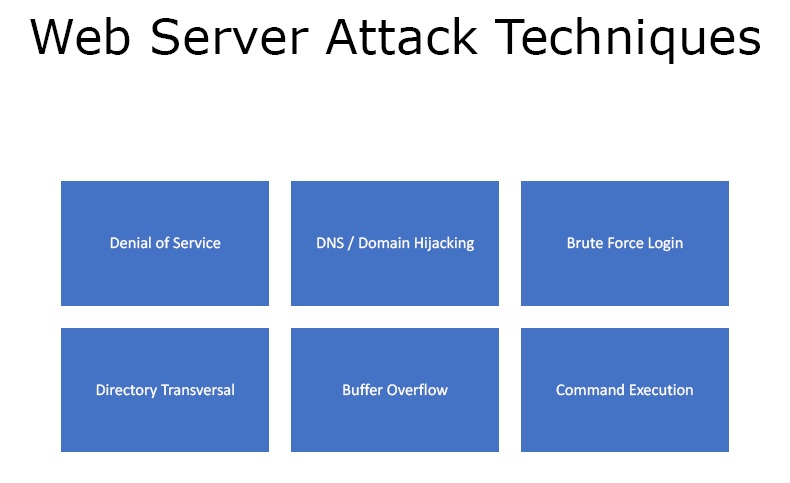 Figure3. Web Server Attack Techniques
Figure3. Web Server Attack Techniques
- Denial of Service
- DNS / Domain Hijacking
- Brute Force Login
- Directory Transversal
- Buffer Overflow
- Command Execution
What is the Impact of Web Server Attacks?
- Reputational Harm – If the website goes offline or it gets defaced or if the user data is stolen, it could lead to loss of reputation for the website.
- “Beachhead” into the network – If the website is hosted on to the corporate network and if it gets hijacked the attacker has access to all the website as well as corporate information.
- Defacement – Many hijackers usually take over the web server and then change the actual landing page with some sort of political, religious or just embarrassing message.
- Data Theft – If we compromise on the web servers, the data is more prone to theft.
- Malware Servicing – If we compromise the web server and there that download malware or Trojans, then it can become a victim of a hijacker easily.
What are the countermeasures?
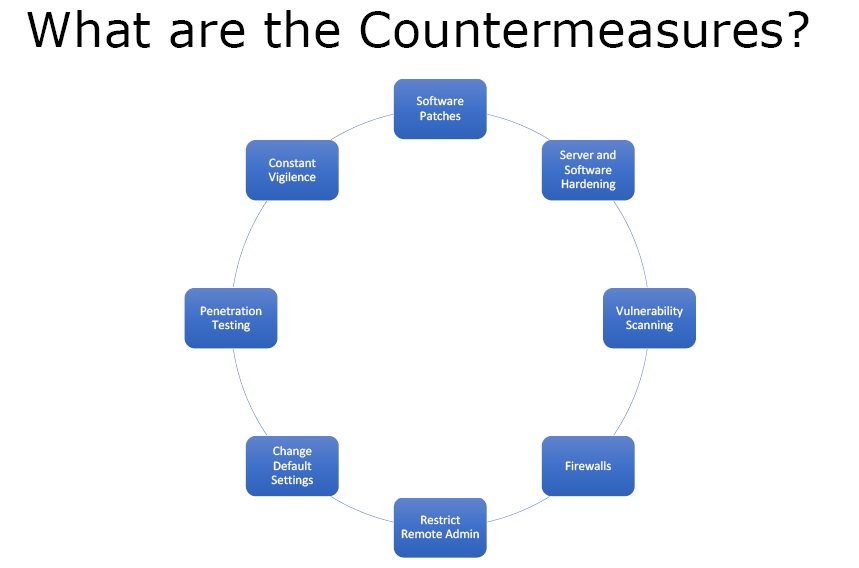
Figure 4. Countermeasures
- Software Patches – One must always patch the software, maintain the web server, and update OS and applications so as to get protection from vulnerabilities.
- Server and Software Hardening – It means that both server and software must perform the task they had to do.
- Vulnerability Scanning – Look for vulnerabilities on the web server.
- Firewalls – There should be a firewall to protect the web server from unwanted attacks.
- Restrict Remote Admin
- Change Default Settings
- Penetration Testing
- Constant Vigilance
Ethical Hacking Tutorial – Hacking Web Servers Theory Video: