What are IDS, Firewall and Honeypot?
- Firewall – A firewall is a network security device that monitors traffic to or from your network. It allows or blocks traffic based on a defined set of security rules.
- IDS – An intrusion detection system (IDS) inspects all inbound and outbound network activity and identifies suspicious patterns that may indicate a network or system attack from someone attempting to break into or compromise a system.
- IPS – An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a system that monitors a network for malicious activities such as security threats or policy violations. The main function of an IPS is to identify suspicious activity, and then log information, attempt to block the activity, and then finally to report it.
- Honeypot – A honeypot is a decoy computer system for trapping hackers or tracking unconventional or new hacking methods
What are different Types of IDS, Firewalls and Honeypots?
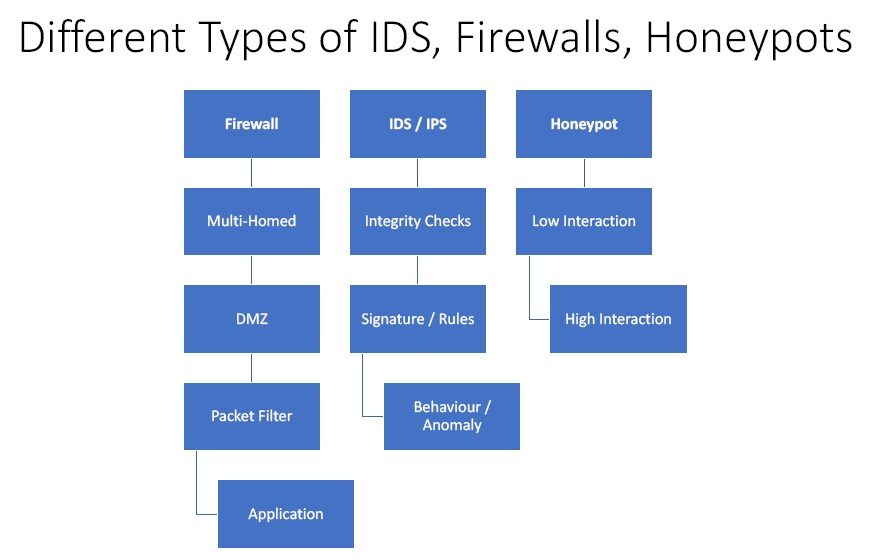
Figure1. Different Types of IDS, Firewalls and Honeypots.
- Firewall
- Multi-Homed – It has two interfaces. One for the trusted network, and other for untrusted network.
- DMZ – It is kind of addition security to the network. The outside world can only see what is being shown by DMZ and the rest is firewalled.
- Packet Filter – It allows the traffic depending upon the type of packet.
- Application – It looks for the content of the packet and look for the malicious code in it.
- IDS / IPS
- Integrity Checks – It monitors a set of system files and looks for changes in it.
- Signature / Rules – It looks for signature rules and then alert the user or block it if it is suspicious.
- Behaviour / Anomaly – In this IDS/IPS is put in learn mode and then it watches the network, system and service for a while. When it is put in detective mode it looks for anomalous behaviour.
- Honeypot
- Low Interaction – One cannot interact with this as an attacker. It just absorbs malware and put them in a file and categorise.
- High Interaction – They are used to actually see how people are hacking into systems.
What are Evasion Techniques?
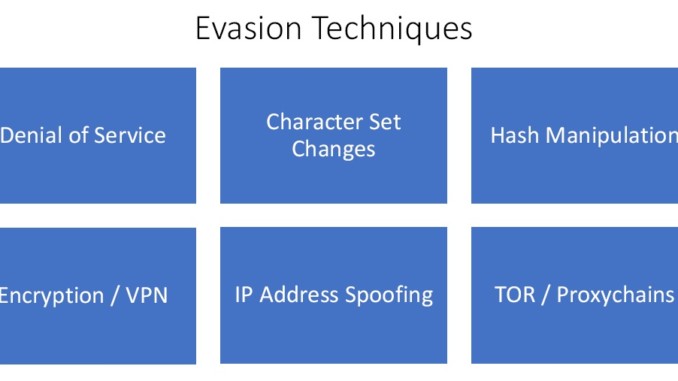
Figure2. Evasion Techniques
- Denial of Service – All the IDSs, IPSs, firewalls and honeypots have vulnerabilities that can be exploited. So they can be taken offline in denial of service.
- Character Set Changes – If we make changes in the character set itself they will pass undetected from all.
- Hash Manipulation – It only looks for specific hashes in the rule. So manipulating them can be used for evasion.
- Encryption / VPN – Once the traffic is encrypted, packet inspection cannot be done.
- IP Address Spoofing – It is spoofing the actual IP address so the people don’t actually know where the attack is originating from.
- TOR / Proxychains – TOR is an anonymous network and proxy chain is a Kali Linux tool through which all the traffic can be routed.
What are the countermeasures?
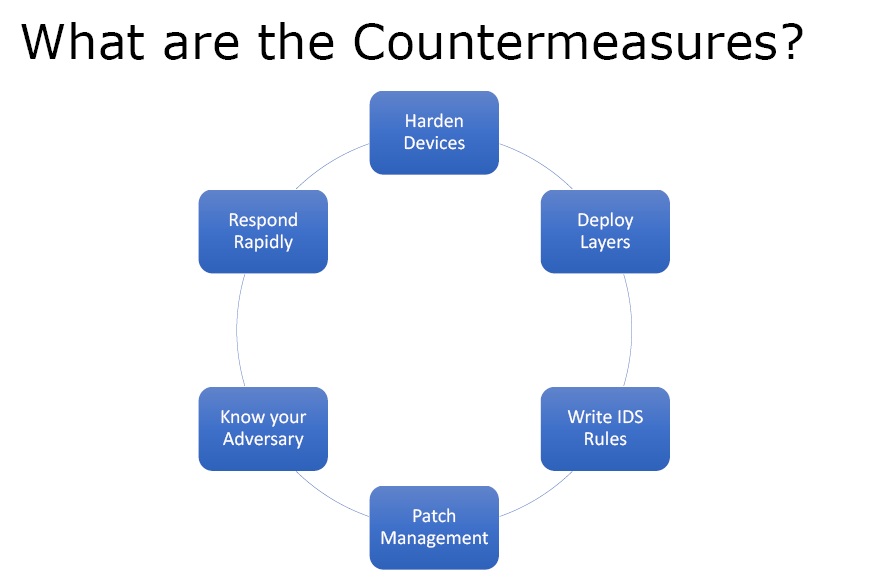
Figure3. Countermeasures
- Harden Devices – This is done by disabling services that are not needed on the actual application server.
- Deploy Layers – Deploy multiple layers of defence and use all the devices like firewalls, IDS, IPD, Honeypots, etc.
- Write IDS Rules – Based on the type of attacks IDS rules can be written that are specific for the organisation.
- Patch Management – If the software and services are up-to-date one is less vulnerable.
- Know your Adversary
- Respond Rapidly – Respond very fast to any kind of security alert.
Ethical Hacking Tutorial – Intrusion Detection Systems, FireWalls, HoneyPots Theory Video: