What are Wireless Concepts?
Figure1. Wireless Concepts
- Extension to the Wired LAN – The wireless network could be a standalone network or an extension of the wired LAN. The aim of the penetration tester is to plug in to the target’s network without actually being at the target side. If one is at the wireless range of the target, one can get some wireless activity going and sniff it.
- Controller / Access Points – In a corporate enterprise environment there will be multiple access points but generally one or two controllers. So once the access to the controller is achieved, one can access all the access points.
- Hotspot – A hotspot defines an area within the Wi-Fi coverage.
- Line of Sight – It is a point-to-point wireless generally also for large enterprise customers.
What are Wireless Standards?
 Figure2. Wireless Standards
Figure2. Wireless Standards
- 11 A – This is first standard or series that operated off the five gigahertz frequency.
- 11 B – – It provided data rate of up to 11Mbps in the 2.4GHz band with DSSS with CCK modulation scheme and WEP & WPA security.
- 11 G – It provided data rate of up to 54Mbps in the 2.4GHz band with OFDM above 20Mbps, DSSS with CCK below 20Mbps modulation scheme and WEP & WPA security.
- 11 N – It provided data rate of up to 300Mbps in the 2.4 and 5GHz. It used channel bonding and allows to wireless bands to be bonded.
- 11 AC – It is the latest and utilizes dual-band wireless technology.
What are Wireless Components?
 Figure3. Wireless Components
Figure3. Wireless Components
- SSID – It is the name that is broadcasted to the wireless clients.
- Open – An open wireless usually does not have any encryption. Thus all the traffic that is floating through it can be sniffed. It also does not have any authentication so anyone can connect to it.
- Shared Key – It is generally encrypted but is quite weak.
- Authorization Services – In this we use a third party to actually do the authentication and clients are registered via some form of certificates. It is highly encrypted.
- BSSID (MAC) – It is the MAC address of the access point.
What are Wireless Encryption Techniques?
 Figure4. Wireless Encryption Techniques
Figure4. Wireless Encryption Techniques
The first encryption that came out in 1997 is Wide Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol. It was a standard set to encrypt wireless traffic. But it used a very small encryption key so the algorithm was quite easy to crack. Due to this in 2003 and 2004 WPA and WPA (2) were created respectively. The previous issue was resolved in these with the use of very low key. The encryption protocol used in WPA 2 was TKIP ( Temporal Key Integrity Protocol). It was designed to provide more secure encryption then WEP. Over time AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) became the standard. There is one more protocol called EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) and it is an authentication framework which is frequently used in wireless networks and point-to-point connections.
What are Wireless Hacking Objectives?
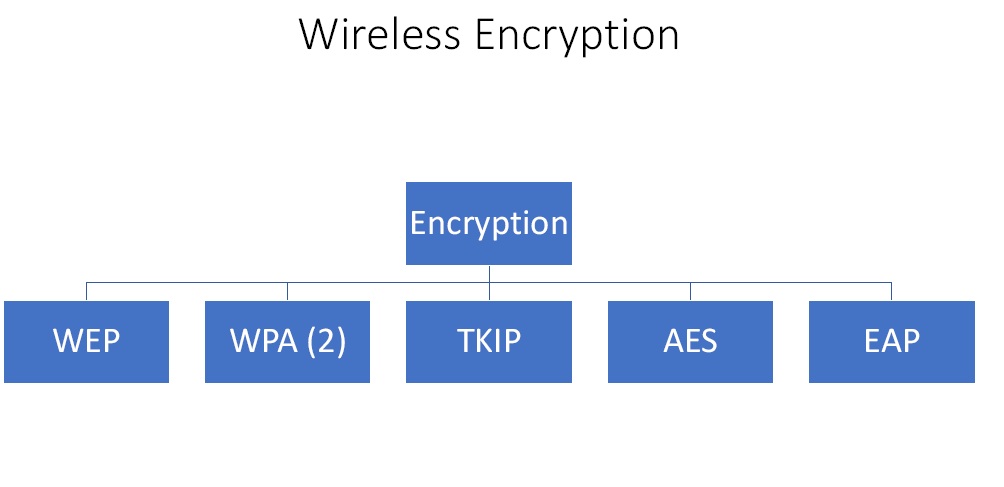 Figure5. Wireless Hacking Objectives
Figure5. Wireless Hacking Objectives
- Availability
- AP Theft
- Denial of Service
- Network Flood
- ARP Poisoning
- Confidentiality
- Sniffing
- MITM
- Rogue AP
- Integrity
- Data Replay
- Packet Injection
- Malware
- Authentication
- PSK Crack
- VPN Login
- Brute Force Key
- Domain Attacks
What are the Countermeasures?
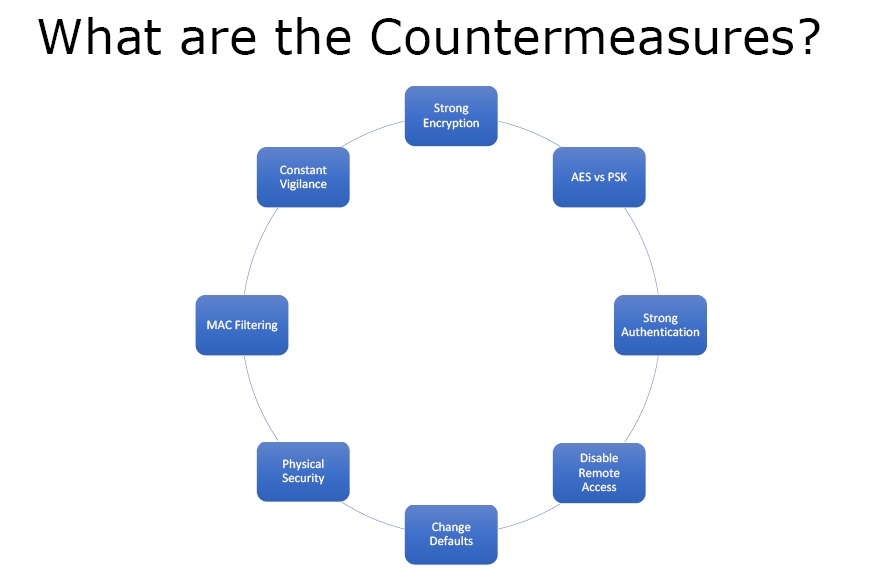 Figure6. Countermeasures
Figure6. Countermeasures
- Strong Encryption – With strong encryption the one way left with the attacker to hack the wireless network is to crack the password.
- AES vs. PSK – AES is better than PSK because PSK can be guessed.
- Strong Authentication – One should use the keys which have at least 10 to 15 characters. The longer the password the longer it will take to crack it.
- Disable Remote Access – One should not have remote access unless there is an important business need for it.
- Change Defaults – A lot of access points and wireless routers have default usernames and passwords. These should be changed because if someone gets to the login page of the router he can easily login to the network.
- Physical Security – Keep the Aps in the secure areas especially for the enterprises.
- MAC Filtering – In order to protect the clients, make an allowable MAC filtering list where only set number of clients is allowed access.
- Constant Vigilance – One must monitor and look at the logs regularly.
Ethical Hacking Tutorial – Wireless Theory Video: